Connecting Milesight UC300 to KaaIoT via TTN
- Introduction
- UC300 interfaces overview
- Payload formatter basics for UC300
- Practical examples
- Practical use case: Smart Greenhouse Irrigation Control
- Sensors connected to UC300
- Actuators connected to UC300
- How it works
- Benefits
- Conclusion
Introduction
The Milesight UC300 is an industrial controller designed for monitoring and controlling field equipment.
It combines multiple input/output interfaces with LoRaWAN or 3G/4G connectivity, making it a flexible building block for industrial automation projects.
In this article, we will not attempt to cover every possible connectivity option. Instead, we provide a brief overview of LoRaWAN connectivity.
Detailed instructions for device setup, TTN registration, and step-by-step KaaIoT integration are beyond the scope of this discussion.
These topics will be covered in a dedicated tutorial later.
Here we will:
- Review UC300 interfaces and their role in industrial automation.
- Show how to work with payload formatters for uplinks and downlinks.
- Provide one practical uplink example and one downlink example.
- Demonstrate a real-world use case for UC300 in smart greenhouse monitoring and control.
UC300 interfaces overview
The UC300 offers a rich set of interfaces that make it suitable for a wide variety of industrial use cases:
- RS232/RS485 — Connecting industrial devices and sensors via Modbus RTU (e.g., energy meters, temperature sensors, PLCs).
- Digital Inputs (DI) — Monitoring discrete signals such as emergency stop buttons, limit switches, or door sensors.
- Digital Outputs (DO) — Controlling external actuators such as relays, lights, or alarms.
- Analog Inputs (AI) — Accepting analog signals (4–20 mA, 0–10 V) for sensors like pressure, level, or flow meters.
- Relay Outputs — Direct control of electrical loads (pumps, valves, fans, heaters).
- LoRaWAN connectivity — Main communication channel to transmit data to TTN and receive commands from the cloud.
This combination makes UC300 a universal gateway between industrial signals and IoT platforms like Kaa.
Payload formatter basics for UC300
UC300 produces binary payloads that need to be decoded before they can be used by IoT applications.
Similarly, control commands must be encoded into binary form before being sent to the device.
Milesight provides official payload formatters for the UC300 series on GitHub:
- Uplink decoder — translates raw LoRaWAN bytes into structured JSON telemetry.
- Downlink encoder — translates JSON command objects into binary payloads UC300 understands.
⚠️ Important: Some documentation examples contain inconsistencies.
For example, the reboot command may be shown as{ "reboot": 1 }, but the encoder expects{ "reboot": "yes" }.
Always validate against the official formatter code.
Practical examples
Uplink example: Monitoring an analog input
Suppose UC300 is connected to a pressure transmitter via its analog input.
The device periodically sends measurement data over LoRaWAN.
- Raw payload (received in TTN as byte array):
0D0248040000 0B0290030000 - Decoded JSON (using uplink formatter):
{ "adc_1": 9.12, "adv_1": 10.96 }
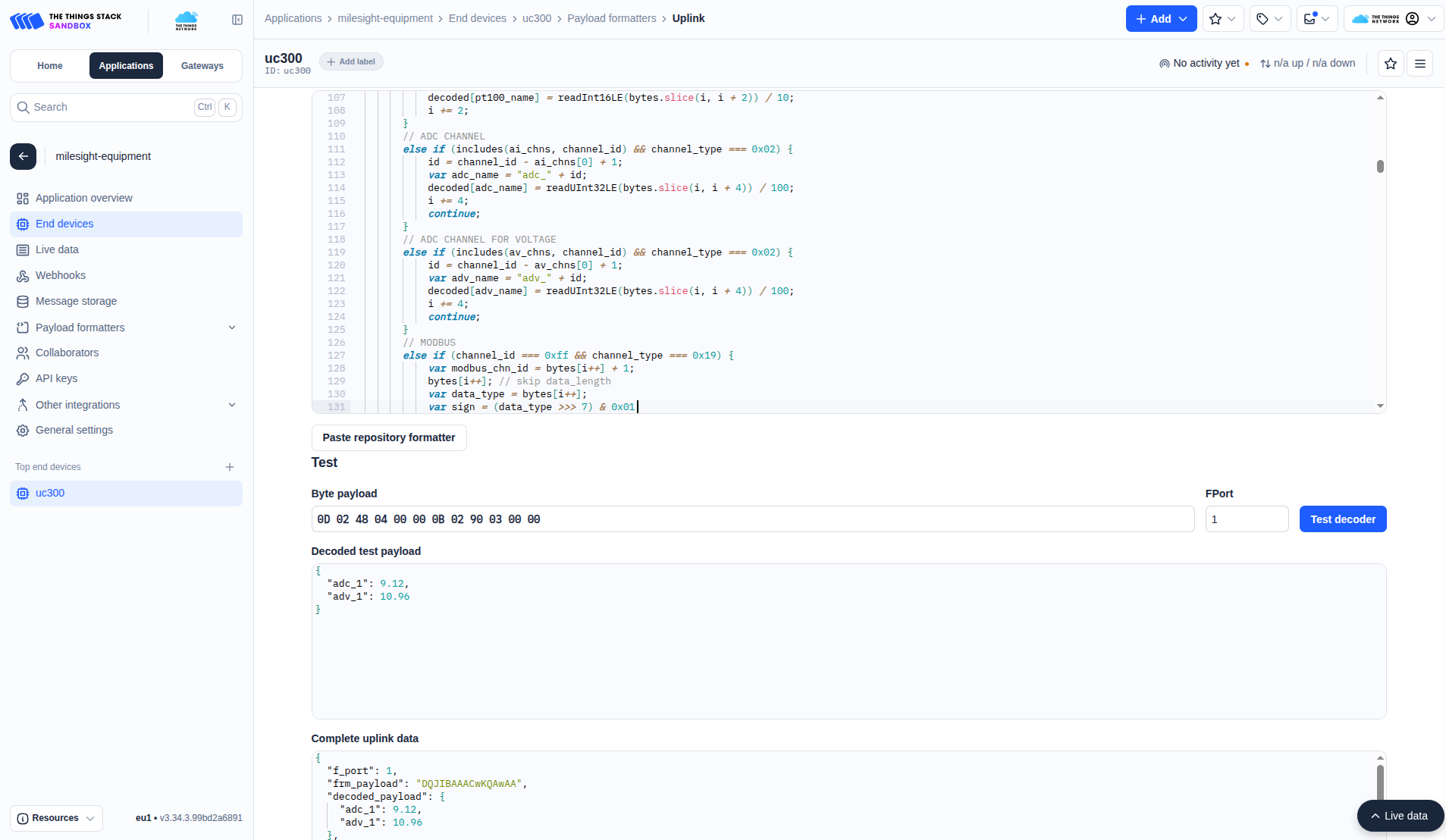
This makes the measurement immediately usable in KaaIoT dashboards and analytics.
Downlink example: controlling a digital output
Now suppose we want to turn on a pump connected to UC300’s relay output.
- JSON command (before encoding):
{ "gpio_output_1": "on", "gpio_output_2": "off", "confirmed": "false", "f_port": 50 } - Encoded payload (bytes) - generated by the downlink encoder before being sent through TTN:
0701FF0800FF
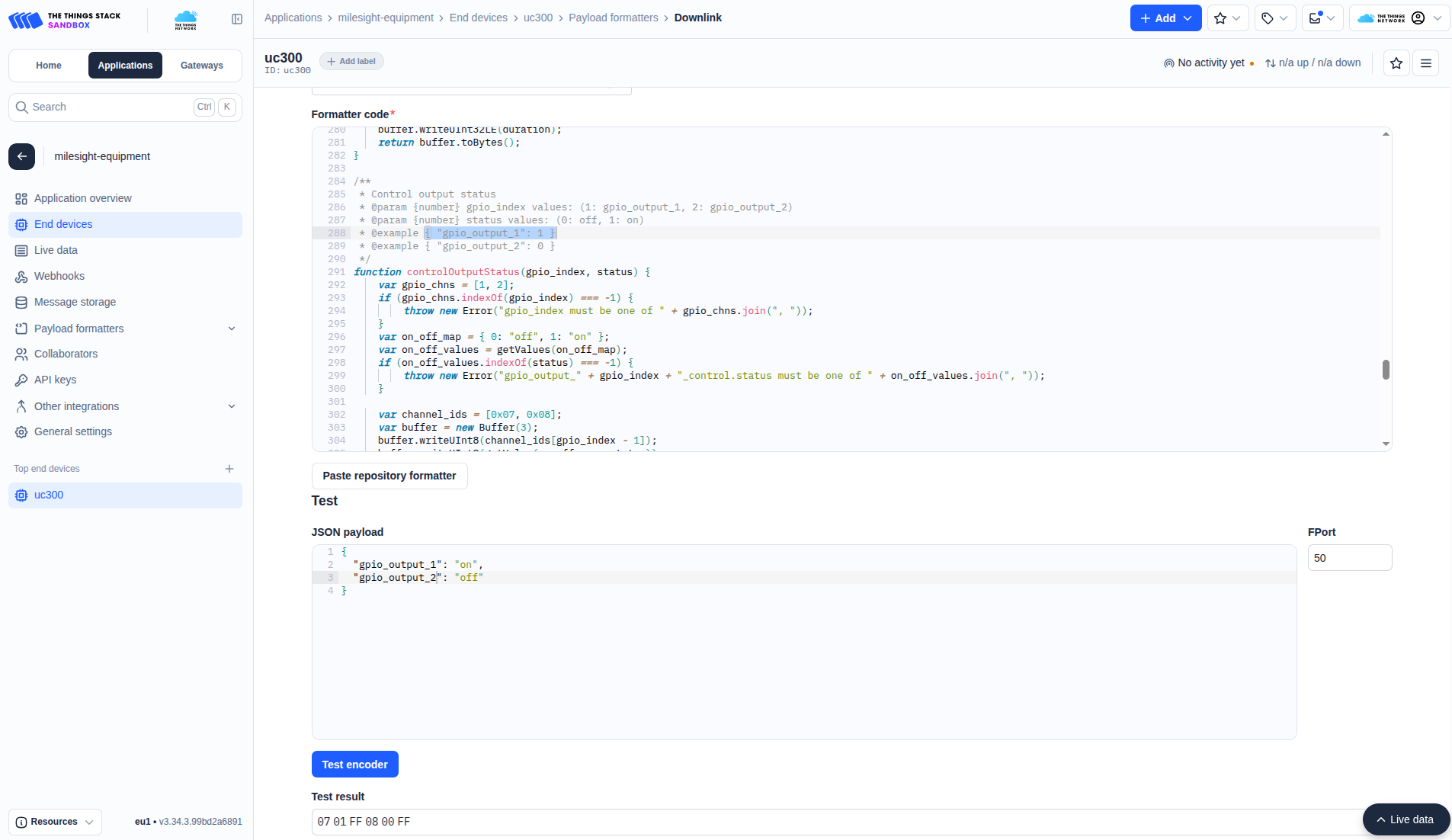
This downlink allows the Kaa platform to remotely control industrial equipment through UC300.
Practical use case: Smart Greenhouse Irrigation Control
The goal is to automate irrigation in a greenhouse based on environmental conditions. The UC300 acts as a local controller, collecting data from sensors and controlling actuators such as pumps and valves, while also transmitting telemetry to a remote LoRaWAN network server for monitoring and optimization.
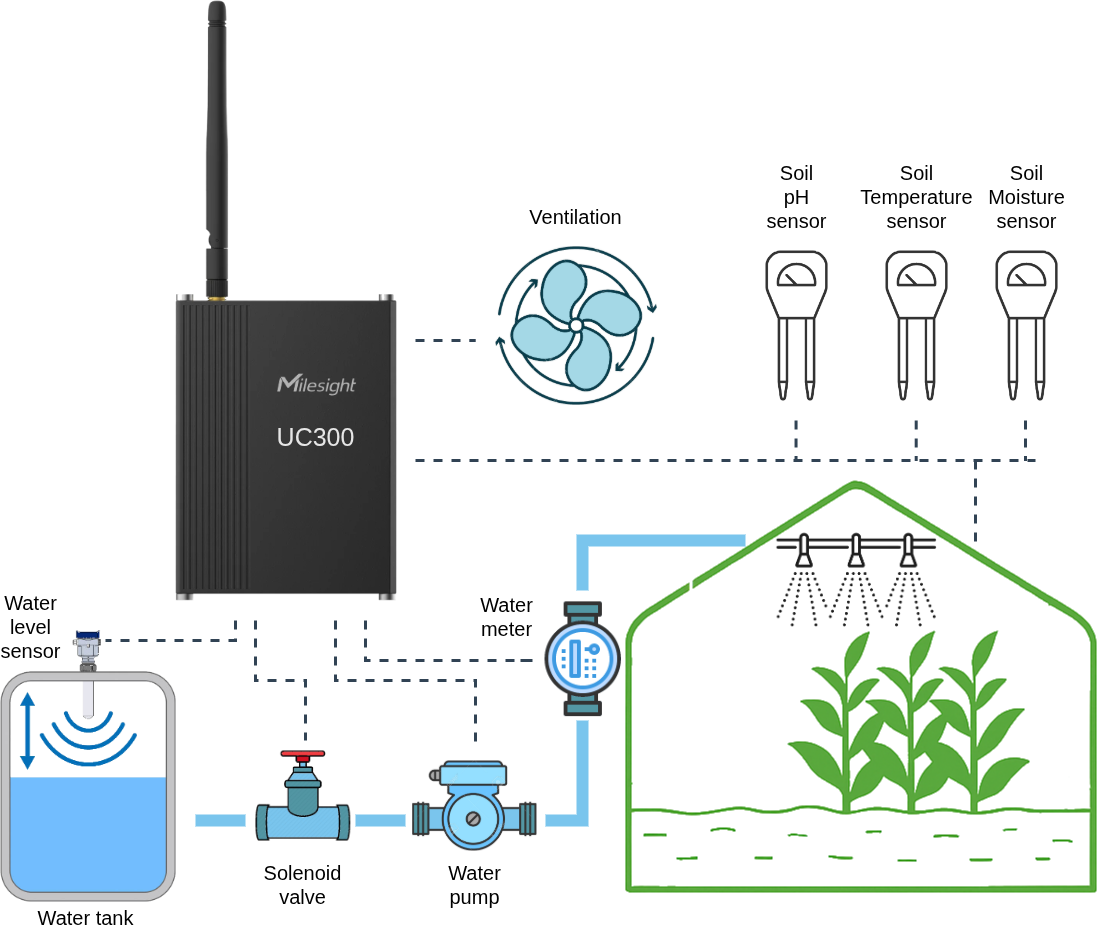
Sensors connected to UC300
-
Soil Moisture Sensors (analog input 0–10 V or 4–20 mA)
Placed in different greenhouse zones to measure soil humidity. -
Soil Temperature Sensor (analog input)
Helps optimize irrigation (water uptake depends on soil temperature). -
Water Tank Level Sensor (analog input or RS485 Modbus RTU)
Ensures there is enough water before activating the pump. -
Ambient Temperature & Humidity Sensor (RS485 Modbus RTU)
Provides environmental data for irrigation scheduling and ventilation control. -
Water meter (RS485 Modbus RTU)
Precisely controls water consumption.
Actuators connected to UC300
-
Water Pump (relay output)
Main pump to supply water for irrigation. -
Solenoid Valves (relay outputs)
Control irrigation for different greenhouse zones independently. -
Ventilation Fan (relay output, optional)
Provides extra climate control if temperature/humidity exceed thresholds.
How it works
- UC300 periodically reads all sensor values and uses them for internal automation logic.
- If the soil moisture drops below the threshold AND the water tank level is sufficient:
- UC300 activates a Pump (Relay 1).
- UC300 opens the required solenoid valve (Relay 2 or Relay 3) for a defined irrigation cycle.
- If the greenhouse temperature exceeds a specified threshold, UC300 activates the ventilation fan (Relay 4).
- All sensor readings and actuator states are sent via LoRaWAN uplink to the Kaa platform via The Things Stack.
- In KaaIoT, this information can be displayed on dashboards and stored for analytics purposes.
- The Operator via the Kaa platform (or automation rules configured in Kaa) can send remote commands (downlinks) that override local automation:
- Start/stop irrigation manually.
- Adjust soil moisture thresholds.
- Change irrigation schedule.
Benefits
- Autonomous operation: even without a network connection, UC300 executes rules locally.
- Remote monitoring: all data visible on the Kaa IoT platform.
- Energy-efficient: LoRaWAN ensures long-range, low-power communication.
- Scalable: more sensors and valves can be added for different greenhouse zones.
This illustrates how UC300 can serve as both a monitoring and a control device, with KaaIoT providing visualization, analytics, and remote operation.
Conclusion
Milesight UC300 is a versatile industrial controller that can bridge field devices with IoT platforms.
By combining multiple I/O interfaces and LoRaWAN connectivity, it enables both data acquisition and remote control.
The key to successful integration with TTN and KaaIoT lies in the proper use of payload formatters.
They allow developers to translate between binary device payloads and structured data or commands.
