Configuring Online/Offline State Handling
- Overview
- Disconnection event handling configuration
- Lifecycle events and connectivity state
- Time-series mapping configuration
- How it works together
Written by Pavlo Anikeichyk
Overview
The Kaa platform allows you to monitor device connectivity and track when endpoints are online or offline.
This is useful for device presence monitoring, alerting, and analytics.
To use the online/offline status, configure settings in either the Base configuration or an Application version configuration.
Base configuration vs. Application version configuration
- The Base configuration applies by default to all versions of a specific application.
- As soon as you modify the configuration for a specific application version, it overrides the Base configuration.
If you want application-specific settings for online/offline handling, configure them in the application version configuration.
Disconnection event handling configuration
Navigate to: Device management → Applications → {your application} → Base configuration → KPC
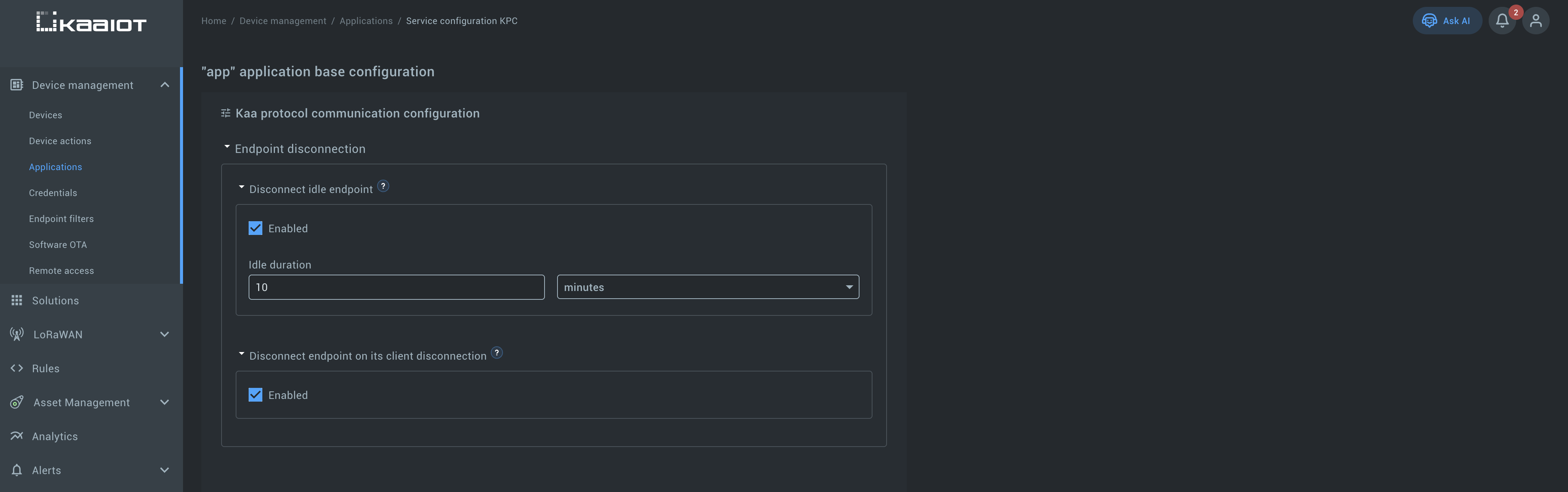
There are two main options under Endpoint disconnection:
- Disconnect idle endpoint
- When enabled, an endpoint will be disconnected after the specified idle duration.
- Useful for LoRaWAN integrations, where the transport connection is always active; if the interval between messages exceeds the idle duration, the platform considers the device disconnected.
- Disconnect endpoint on its client disconnection
- When enabled, the Kaa platform updates the state based on client connection/disconnection events (e.g., MQTT direct connections).
- Not relevant for LoRaWAN, since the integration always keeps the transport connection alive.
Example (Base configuration):
Lifecycle events and connectivity state
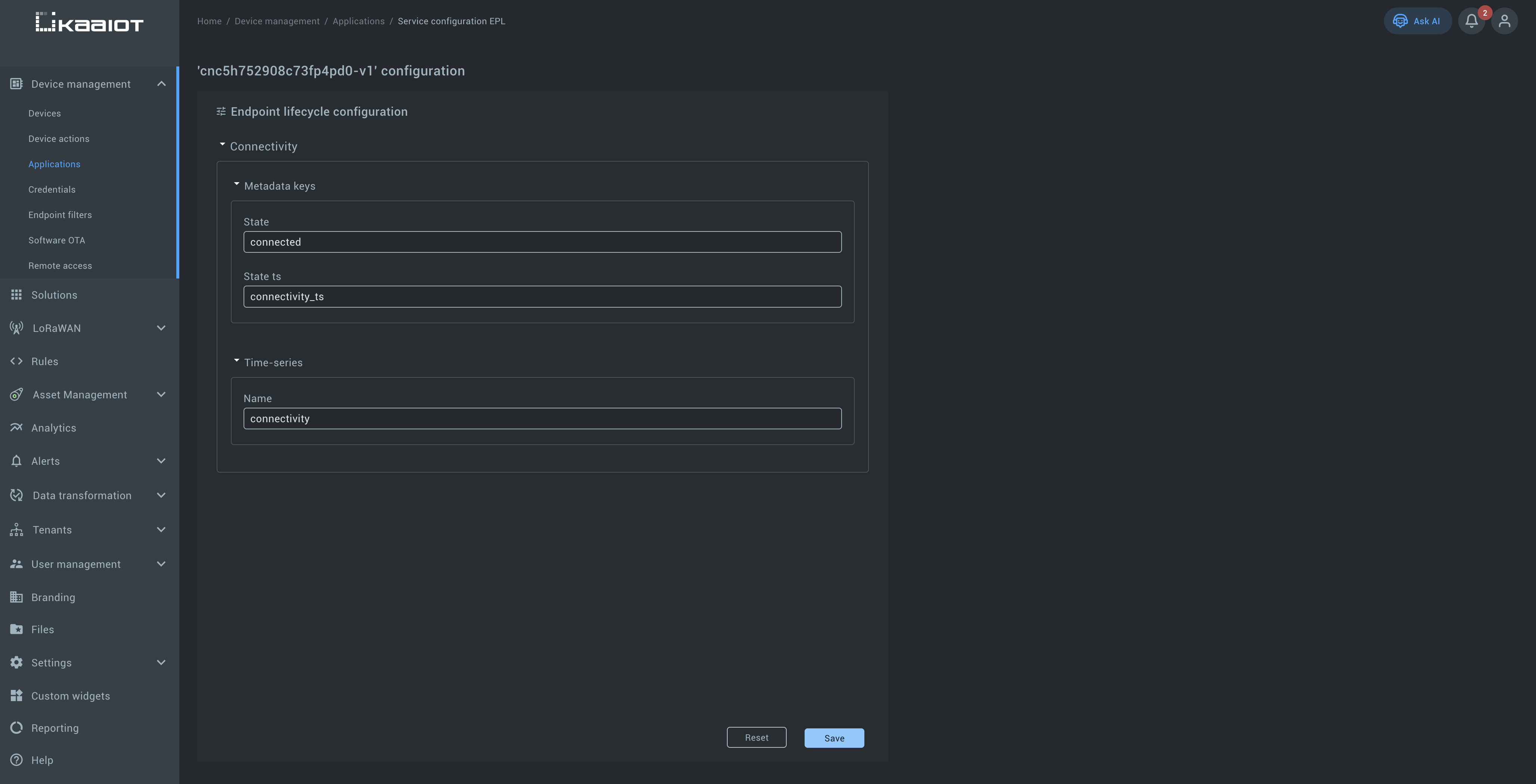
The platform internally generates events when devices connect or disconnect.
In the configuration, you can define:
- Metadata keys – specify the metadata keys to store the connection state (
connected,disconnected) and a timestamp. - Time-series – specify the time-series name to store connectivity changes.
Example (Application version configuration):
Time-series mapping configuration
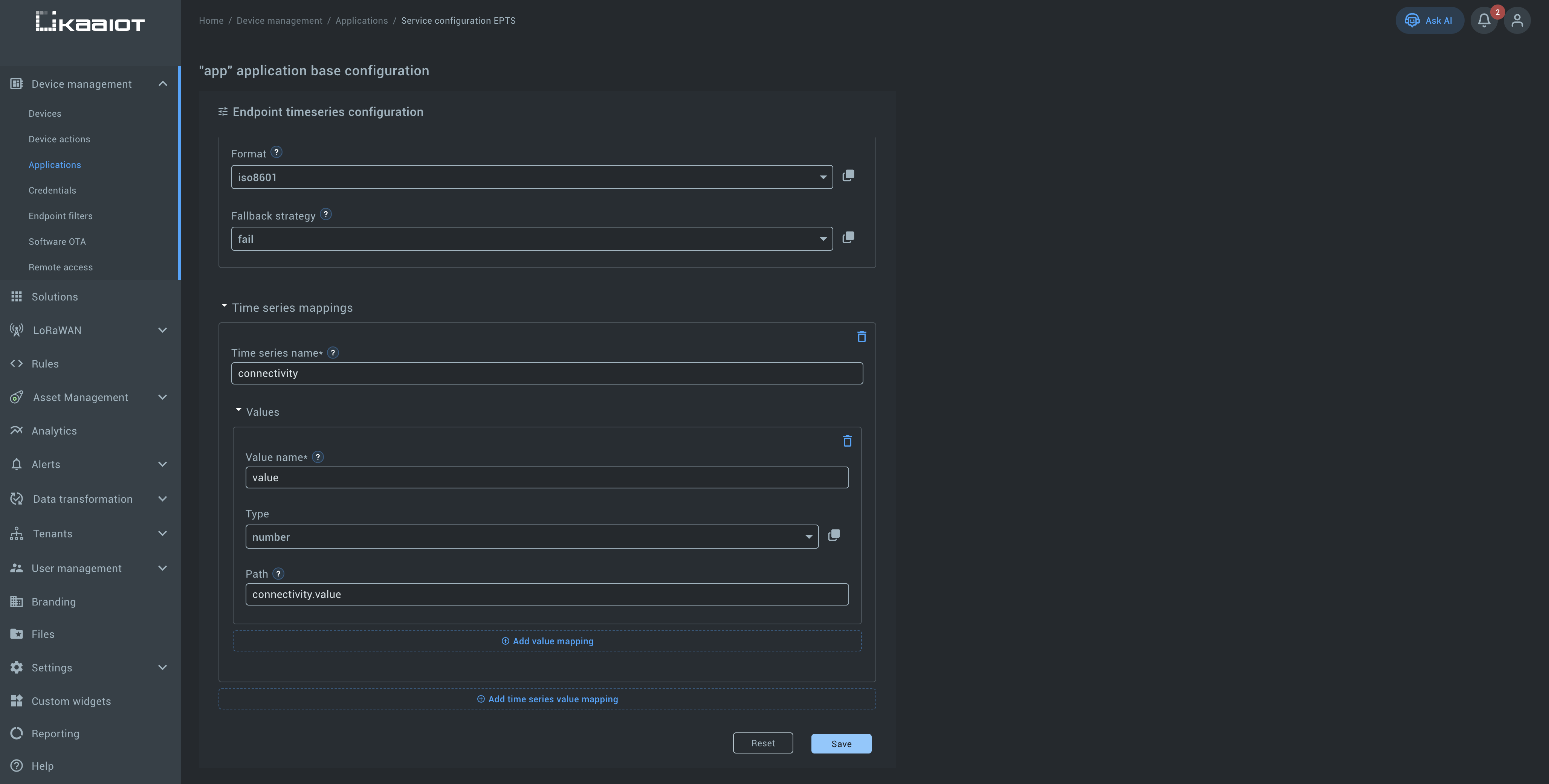
In this example, we show the configuration for mapping the connectivity state to time-series values.
The configuration includes:
- Time-series name – e.g.,
connectivity. - Value mapping – maps
connectivity.valueinto numeric values.
Example (Base configuration):
How it works together
- The platform detects endpoint connection or disconnection, either by idle timeout or client connect/disconnect events.
- It then generates endpoint lifecycle events and updates the corresponding metadata and time-series keys.
- Finally, the platform maps connectivity values to time-series for further use.
As a result, you can always see the device connectivity state, both in metadata and in time-series storage.
Remember: The Base configuration applies globally until you modify an application version configuration, which then overrides the base settings.



