User Management Example
- Overview
- Admin
- Creating Manager Account
- Create Developer Account
- Create Customer Account
- Customer Policies
- Summing Up
Overview
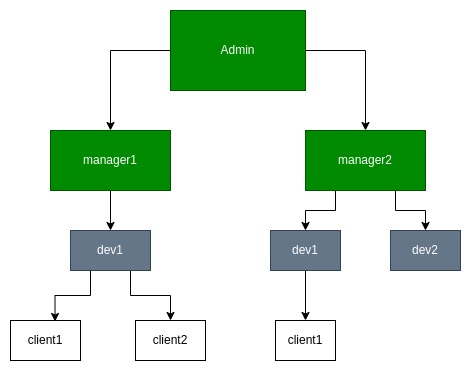
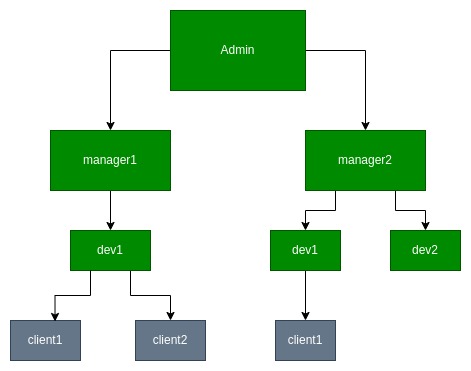
This tutorial shows how to build a structured user hierarchy in Kaa using tools from User Management Terms and Concepts. We’ll set up a role-based access model like the one shown below:
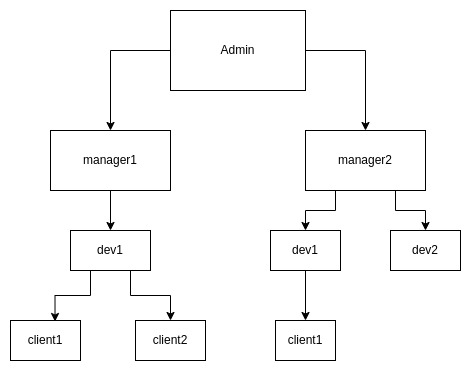
User Roles
- Admin – Full access across the entire infrastructure.
- Manager – Can manage resources and users within their own scope.
- Developer – Can work with resources assigned by the manager and assign them to clients.
- Client – Has read-only access to assigned resources.
Admin
Log into your Kaa account and go to User Management -> User.
You’ll see one default user account. That’s your Admin account (e.g., testadmin). From here we’ll start distributing access.
Creating Manager Account
Managers need permissions to create resources, manage users, and assign policies within their own scope.
To create manager:
- While logged in as Admin, create a manager user (for example, manager1).
- Set the manager user directory to /manager.
Create Manager Policies
-
Basic Policy for all Managers:
First, let’s define the general access for all managers.
Navigate to User Management -> Policies and click Add Policy.
Name the policymanager-basic-access.
Add a Statement, and click the JSON view tab and paste the JSON below, replacing<tenant-id>with your actual tenant ID.{ "statements": [ { "effect": "allow", "description": "UI access", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>:*" ], "actions": [ "ui:*" ] }, { "effect": "allow", "description": "Access to create it's own endpoints", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>::endpoint/*" ], "actions": [ "endpoint:create", "endpoint:delete", "endpoint:update" ] }, { "effect": "allow", "description": "Allows creation of policies", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:iamcore:<tenant-id>::policy/*" ], "actions": [ "iamcore:policy:*" ] }, { "effect": "allow", "description": "Access to create applications", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>::application/*", "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>::tenant/system", "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>::tenant-system/tenant-system" ], "actions": [ "application:create", "tenant:application:create" ] } ] }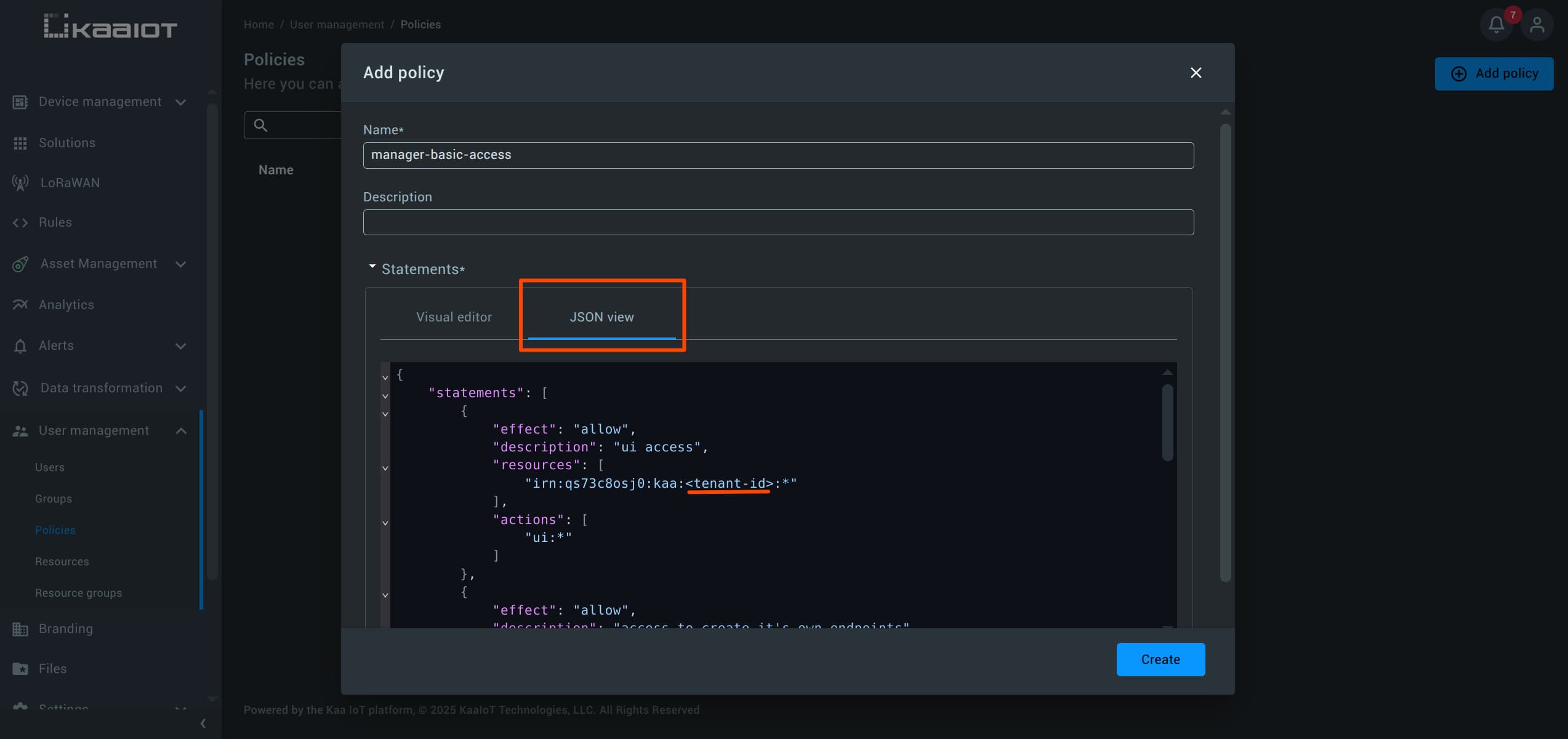
-
Policy for a Specific Manager
Create a unique policy for each manager to keep their access isolated.- Name the policy something like
manager1-resources. - As in step one (Basic Policy for all Managers), paste the JSON below, replace
<tenant-id>. Also make sure the user directory path matches that manager’s directory.
{ "statements": [ { "effect": "allow", "description": "Grants full access to users within manager1 hierarchy", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:iamcore:<tenant-id>::user/manager/manager1", "irn:qs73c8osj0:iamcore:<tenant-id>::user/manager/manager1/*" ], "actions": [ "iamcore:user:*" ] } ] }After creating the policy, assign it to
manager1. Then, log in to themanager1account and verify that you can create applications and endpoints. - Name the policy something like
Take a quick look at what each policy is for.
Each one uses certain actions. You can check what those actions mean in this document.
Create Developer Account
Now let’s create a developer account.
Developers can create and manage devices assigned to them.
Use the Manager account to set up access.
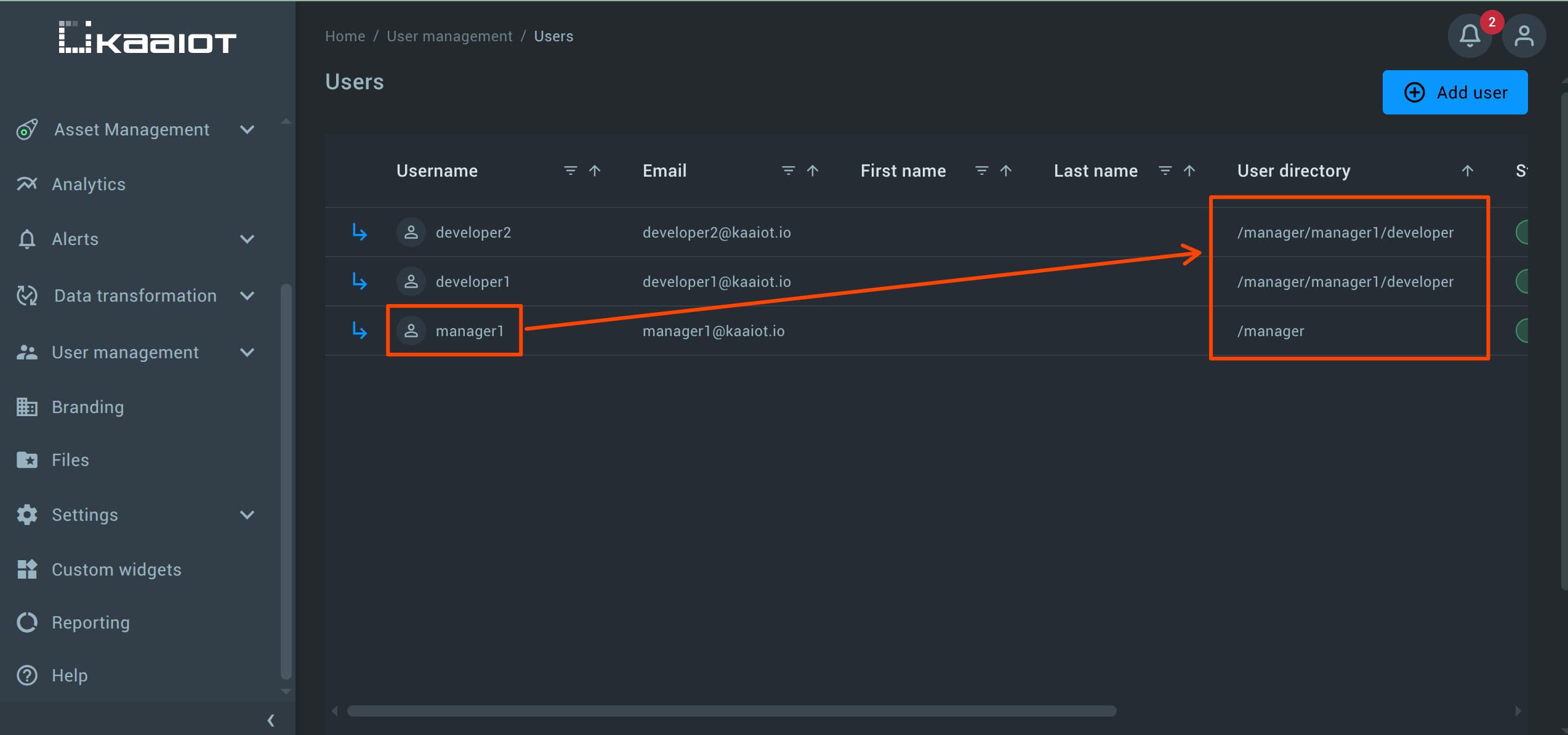
Go to User Management -> Users and create at least one developer account (e.g., developer1).
Make sure the user directory for each developer is set to:
/manager/<managers_username>/developer
If the user directory is incorrect, account creation will fail due to permission restrictions.
That’s because the manager1-resources policy we created earlier only allows access to the /manager/manager1/* directory.
Create Resources for Developer
As manager, create an application and add endpoints, so that we have something to work with and share with the developer.
Note: If you’re not familiar with endpoints and applications, check out the Getting Started Guide.
Create Developer Policy
-
Base Policy for Developer
While logged in as the manager, go to User Management -> Policies -> Add Policy.
In JSON view, paste the base policy code:{ "statements": [ { "effect": "allow", "description": "Full access to UI", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>:*" ], "actions": [ "ui:*" ] }, { "effect": "allow", "description": "Access to create endpoints", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>::endpoint/*" ], "actions": [ "endpoint:*" ] }, { "effect": "allow", "description": "Access to create policies", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:iamcore:<tenant-id>::policy/*" ], "actions": [ "iamcore:policy:create", "iamcore:policy:read", "iamcore:policy:update", "iamcore:policy:user:attach", "iamcore:policy:user:detach" ] } ] } -
Developer-Specific Policy
In JSON view, paste the following and make sure to:- Replace
<tenant-id> - Ensure
userDirectorymatches your developer path (/manager/manager1/developer/developer1) - Replace
<application-id>with the ID of the application you created earlier. Read more about Application ID here.
{ "statements": [ { "effect": "allow", "description": "Full access to the application", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:kaa:<tenant-id>::application/<application-id>" ], "actions": [ "*" ] }, { "effect": "allow", "description": "Full access to users within developer1 directory", "resources": [ "irn:qs73c8osj0:iamcore:<tenant-id>::user/manager/manager1/developer/developer1", "irn:qs73c8osj0:iamcore:<tenant-id>::user/manager/manager1/developer/developer1/*" ], "actions": [ "iamcore:user:*" ] } ] } - Replace
-
Assign both policies to the
developer1and log in with that account.
Create Customer Account
Customers will have read-only access to resources assigned by the developer.
We’ll create the customer account using the developer1 account.
Log in to the developer1 account, then go to User Management -> Users and create the customer1 account.
Customer Policies
Customer policies are simple and involve resources created with developer1.
For policy creation, we’ll use the Visual Editor instead of the JSON view this time.
While logged into the developer1 account, create the following policies:
customer-basic-accessPolicy
In the Visual Editor, add a statement:- Allow actions:
ui:dashboard:manage,ui:device:manage - Resources: All resources
- Allow actions:
-
customer1-resourcesPolicy
Add two statements:a) Endpoint access
- Allow action:
endpoints:read - Resources: Select specific endpoints to share
b) Application metadata access
- Allow actions:
application:endpoints-metadata-keys:readapplication:read
- Resources: Select the application the endpoints belong to
Save both policies and assign them to the customer.
The customer will only have access to the specified endpoints and minimal UI functionality. - Allow action:
Summing Up
You’ve now set up a complete User Management architecture:
- Admin can manage everything
- Manager can manage developers
- Developers can manage and assign resources to customers
- Customers have limited read-only access
Use the provided JSON examples to share or restrict resources as needed.
